Regenerative Meat
With every dollar we spend, we choose what system we support.
What does Regenerative Meat actually mean?
Regenerative meat refers to meat that is produced using regenerative agriculture practices that aim to rebuild soil health, reduce carbon emissions, and promote biodiversity. This type of meat is often produced using rotational grazing methods that mimic the natural grazing patterns of wild animals, and is typically free from antibiotics and hormones.
What is regenerative agriculture?
In the 1980s, the Rodale Institute coined the term “regenerative agriculture”, but the ethos and practices of this movement have been the norm in many Native and Indigenous communities for centuries.
At its core, regenerative agriculture revolves around the belief that agriculture can only be truly sustainable when we work with the land, instead of viewing nature as a limitless resource we can constantly take advantage of.
Benefits of Regeneratively Raised Meat
By promoting healthy soil, regenerative agriculture practices can help:
Restore topsoil and ecosystems
Sequester carbon into soil
and is often higher in nutrients and free from harmful additives, making it a healthier choice for consumers.
Are there nutritional benefits to eating regeneratively raised beef?
Here at Grass Roots Farmers Co-op, our regeneratively-raised beef is 100% grass-fed and finished. Our cattle are free to graze on non-GMO pasture, outside in the sunshine as nature intended, every single day. They never eat grain or grain by-products, and are never treated with antibiotics or hormones.
Multiple studies have confirmed that cattle raised under these conditions are more flavorful than conventionally-raised beef. In addition, studies have also shown that regenerative beef also provides several nutritional benefits, such as:
Glutathione, also known as the “Master Antioxidant”
Significant source of L-Carnitine
High in protein and several minerals
Carnosine, CLAs and Creatine
Rich in B vitamins
Health and Environmental Benefits of Regenerative Farm Meat
Health Benefits:
Leaner and Nutrient-Rich: Regenerative meats are often leaner and contain higher levels of essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. They typically have lower levels of saturated fats compared to grain-fed meats.
No Antibiotics or Hormones: Regenerative farming practices prioritize animal health, reducing the need for antibiotics and synthetic hormones. As a result, the meat is less likely to contain residual antibiotics or hormone residues that can potentially affect human health.
No Synthetic Chemicals: Regenerative meat production avoids the use of synthetic pesticides and herbicides. This means that consumers are less exposed to potentially harmful chemical residues commonly found in conventionally raised meat.
Improved Animal Welfare: Animals raised using regenerative practices are often provided with more natural living conditions, access to open pastures, and humane treatment, contributing to the ethical treatment of animals which leads to less need for pharmaceutical inputs and less health issues.
Environmental Benefits:
Carbon Sequestration: Regenerative agriculture emphasizes soil health and carbon sequestration. Healthier soils can store more carbon, mitigating climate change by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Reduced Erosion: Practices like cover cropping and reduced tillage help prevent soil erosion, which can lead to sedimentation in water bodies and the loss of fertile topsoil.
Enhanced Biodiversity: Regenerative farms often support a wide variety of plant species, providing habitats for pollinators and wildlife. Increased biodiversity promotes ecosystem resilience and contributes to overall environmental health.
Water Quality: By reducing chemical inputs and promoting healthy soil, regenerative farming practices can help improve water quality by reducing nutrient runoff into rivers and streams, which can lead to water pollution.
Resilient Ecosystems: Regenerative agriculture encourages the development of resilient ecosystems, which are better equipped to withstand environmental challenges such as droughts and extreme weather events.
How Regenerative Meat makes its Way to Your Plate
If you're interested in trying regenerative meat, there are a number of places where you can buy it. See some of our favorite places to buy here online!
Here are a few options to consider:
-
White Oaks Pastures - THE Ultimate Regenerative Farm and one of the leaders in the movement. Check out their huge array of regenerative meats, tours, stays and about how they transformed regenerative farming for the world! Savory Hub, Humane Certified, and tested and proven carbon negative farm! Visit their site here.
-
Richards Regenerative is 100% grass-fed and grass-finished certified by the American Grassfed Association.
In 2019, RGF became the first ranch west of the Mississippi to receive the Savory Institute's groundbreaking Land to Market™ certification for regenerative ranching.
Richards Regenerative's mission is to provide the highest quality grass-fed beef to their customers and do so in the most transparent and sustainable way possible. The animals are never fed grain, corn products, given antibiotics or growth hormones.
Explore their website to dive deeper into their regenerative farming practices.
-
Located in Eastern Nebraska, we are a regenerative farm committed to producing the highest quality, nutrient dense proteins for our customers. At Back to Nature Farms, we raise 100% grassfed, grass finished beef, pasture raised pork and chicken with a focus on sustainability and animal welfare.
Our philosophy is simple: healthy soils create healthy plants, which in turn nourish thriving animals. This holistic approach allows us to provide you with the finest cuts of meat while supporting the health of our land and ecosystem.
Transparency is at the core of everything we do. From the way we care for our animals to how we process and deliver our products, we believe in being open and honest with our customers every step of the way.
Visit our website at backtonaturefarms.org and Enjoy Free Shipping on Orders Over $249.
Sign up to our emails on our website for any discounts, farm life, new inventory and more!
Experience the difference that regenerative farming makes directly from our farm to your table. -
Pasture-raised. Grass-fed. Fair-wage. Regeneratively raised in the U.S.A.
Grass Roots isn’t just a co-op, it’s a movement. A community of small-scale regenerative farmers working together to fix a broken food system. Every cut of meat is raised on pasture with care, traceable to the farmer who raised it, and shipped straight to your door.
By putting power back in the hands of independent farmers, Grass Roots is restoring soil health, protecting animal welfare, and rebuilding rural economies one farm, one meal, one customer at a time.
Visit GrassRootsCoop.com and get free shipping on orders over $149
Use code COOP15 for 15% off your first $180+ order. -
Pasturebird - Pasturebird is known for being a leader in the regenerative movement and making amazing chicken products available. Visit their site to order or to build a subscription box of regenerative chicken right to your door. Also check out their Instagram for their amazing grazing pictures! Use REGEN10 for 10% off. Visit them here.
-
Rooted in over 50 years of family farming and more than 40 years as a certified organic operation, StarWalker Organic Farms is a proud third-generation ranch leading the way in regenerative agriculture. Our full-circle approach to farming encompasses everything from planting the seeds that feed our livestock to the birth and finishing of our animals. Through our processing plant, StarHarvest Co., and our consumer brand, StarWalker Farms Beef, Pork & Jerky, we’ve built a truly integrated farm-to-table model.
Beyond our livestock, we cultivate organic alfalfa and grain, embodying the belief that food should be raised the way nature intended: Soil to Soul, Nurturing Health Naturally. We are the farm, the processor, and the brand, committed to restoring the land, nourishing people, and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.
https://starwalkerorganicfarms.com/ -
Regenerative Seafood?! What!?
Check out their huge variety of seafood products along with other items like grains, soups, dried fruit, spices, and more. Ready to eat foods never looked so good! Visit them here.
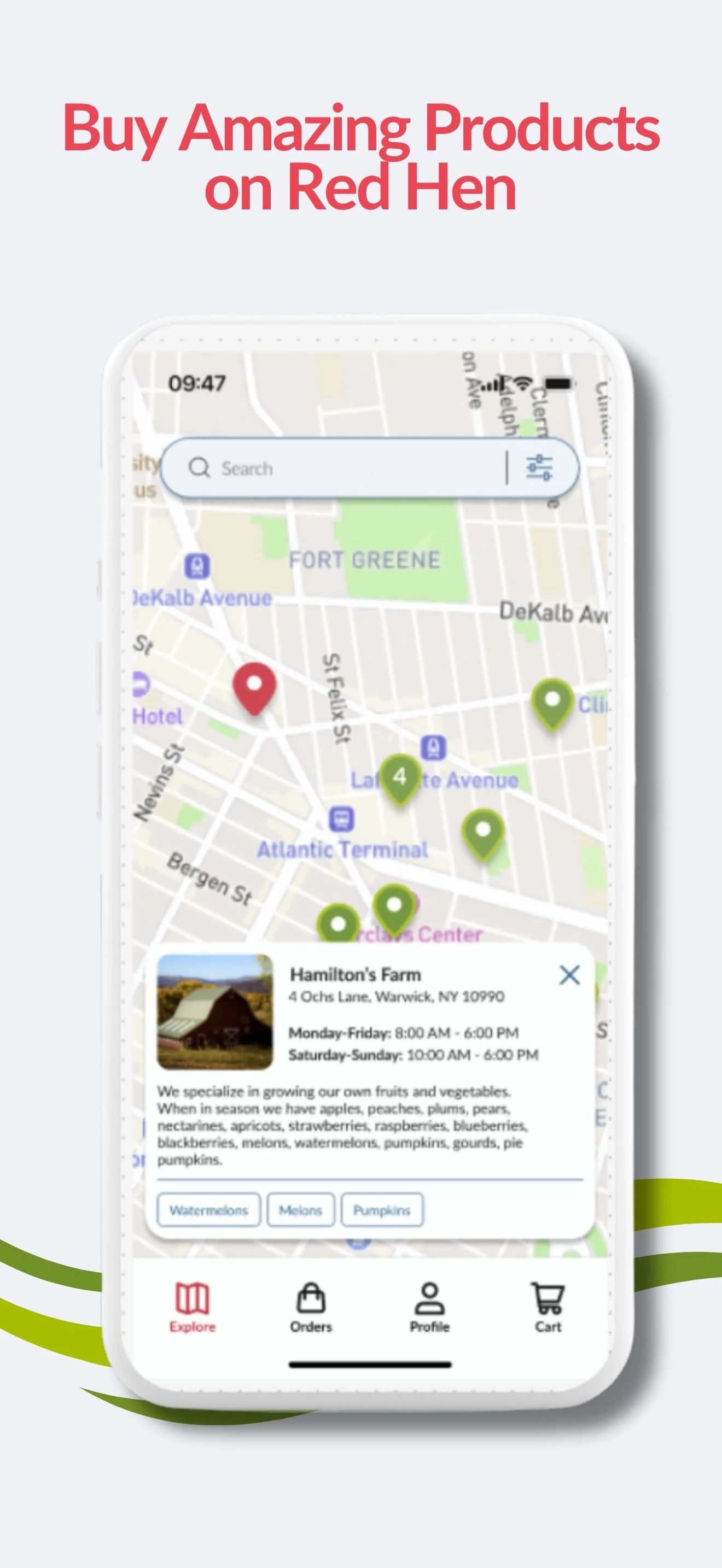
You can also find regenerative meats on the Red Hen App
Red Hen connects you directly with farmers selling verified regenerative meats, without middlemen or subscriptions.
To find what’s available near you:
Open the Red Hen App
Set the Production Method filter to Regenerative
Search by product (beef, chicken, pork, lamb, etc.)
Choose how you want it:
Pickup
Local delivery
Shipping (where available)
You’ll see real farms, transparent practices, and direct pricing — so you can support regenerative producers while sourcing meat that aligns with your values.
Deciphering Labels and Certifications in Meat Products
Here's a guide to understanding regenerative meat labels and certifications:
Regenerative Agriculture Certifications: These are certifications given by specific nonprofits and advocacy groups for the highest level of Regenerative Standards. There’s a few on the market and more emerging.
Grass-Finished: A "Grass-Finished" label indicates that the animals were primarily raised on natural pastures and grazed on grass and forage, rather than being fed grain-based diets. While not exclusive to regenerative practices, grass-fed meat is often associated with more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming methods.
GRASS FED DOES NOT MEAN GRASS FINISHED. This means the cow ate grass during their life, they all do. Look for finishing practices.Local and Farmers' Markets: Consider purchasing meat from local farmers' markets or directly from farmers you trust. Engaging in conversations with producers can provide valuable insights into their farming methods and commitment to regenerative agriculture. Find a farm near you with our map here.
Understanding the Unique Practices in Regenerative Meat Production
Regenerative meat production embodies a holistic and sustainable approach to livestock farming, emphasizing several unique practices:
Rotational Grazing: Regenerative farmers implement rotational grazing systems, moving livestock regularly to different pasture areas. This prevents overgrazing, allows vegetation to recover, and encourages soil improvement. It mimics the natural behavior of herbivores like the buffalo that has huge ecological benefits.
Cover Cropping: Cover crops, like legumes and clover, are, on some farms, sown in between periods of livestock grazing. These plants protect the soil from erosion, fix nitrogen, and improve overall soil structure. They also provide additional forage for animals.
No-Till Farming: Minimizing soil disturbance through no-till or reduced-till farming practices helps retain moisture, preserve beneficial microorganisms, and reduce carbon loss from the soil. Instead of tilling in crops, many farmers use no-till drills to implement cover crops.
Biodiversity Promotion: Regenerative farms encourage biodiversity by maintaining diverse plant, bug, and even animal species, allowing natural vegetation to thrive, and fostering habitats for pollinators and wildlife. This approach creates resilient ecosystems and reduces the need for chemical inputs.
Composting: Effective composting and careful management of animal manure reduce the risk of nutrient runoff and contamination of water sources. Instead, these practices recycle nutrients back into the soil, enriching it naturally. This is largely achieved through rotational grazing.
“It's also important to specify that regenerative farming techniques aren't new. In Indigenous and Native communities, regenerative practices have been the norm since before colonization, regardless of it not having fancy term attached. Regenerative agriculture practices are intrinsic to Indigenous farmers' agricultural practices, which prioritize a relationship with the soil, animals, and people. And it's not about satisfying a checklist; it's the natural way of life and how it's always been done.” - Well + Good
By embracing these practices, regenerative meat production not only yields high-quality, ethically raised meat but also contributes to soil regeneration, biodiversity conservation, and carbon sequestration. It represents a promising model for sustainable agriculture, aligning with the broader goal of building resilient and environmentally friendly food systems.
And last place is always to find Regenerative meat locally!
Check out our map of regenerative farmers near you or get it shipped from amazing farmers above.
Are regenerative meat healthy?
As a result, regeneratively raised meat often contains higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals, including omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Healthy Fats: Animals raised on pasture-based diets typically have a healthier fatty acid profile compared to those raised in confined feedlots.
What does regenerative meat mean?
It basically means the beef cattle have been raised in a regenerative system, one that uses rotational grazing, cover crops, and other “regenerative” techniques that improve soil quality.